
Wastewater management is a vital necessity for commercial properties, ranging from hotels and hospitals to manufacturing facilities and retail centers. These properties often produce significant volumes of wastewater that require reliable treatment solutions, with septic tanks being a necessary choice for many businesses both in cities and rural locations. Designed to handle large scale waste management, commercial septic tanks come in a variety of sizes, including options with capacities of up to 20,000 gallons, to meet the demands of high usage environments.
Commercial septic tanks play an essential role in maintaining sanitation and regulatory compliance across various industries. Hospitality businesses need them to efficiently handle wastewater from guests and staff, while healthcare facilities rely on their systems to manage medical waste. Manufacturing plants, with their unique demands, often require high capacity tanks to ensure smooth wastewater processing. Regardless of the industry, understanding the costs and details of selecting the right septic tank is a top priority for any commercial property owner, contractor, or engineering firm.

This article will explore the factors that influence the pricing of large capacity commercial septic tanks. From tank size and material to site location, installation, and ongoing maintenance costs, we’ll break down everything you need to consider when planning this investment. Whether you are upgrading an existing system, replacing an old tank, or installing at a new site, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions for your property.
Factors Influencing Commercial Septic Tank Pricing
Understanding what drives the cost of commercial septic tanks can help individuals and companies make better decisions and budget effectively. From the size of the tank to specific customizations, several factors shape the final price. Below, we’ll separate these points into key categories to provide a clear picture of what to expect.
Tank Size and Capacity
The size of a septic tank plays a significant role in its cost. Larger tanks, such as those with capacities between 10,000 and 20,000 gallons, are understandably more expensive due to the increased material requirements and larger storage capacity. These large tanks are often needed for commercial properties as they produce much larger volumes of wastewater compared to residential homes. Due to the complexity in calculating the total volume of expected wastewater, engineers and contractors are often involved in determining the septic tank size needed. Some properties will need multiple septic tanks to reach the capacity required for wastewater management.
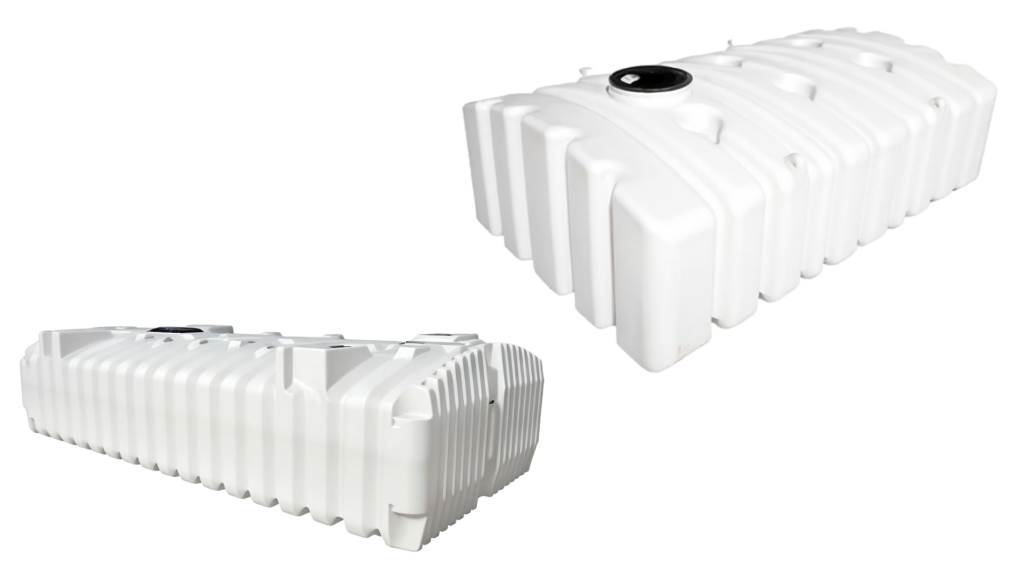
Material of the Tank
The material that the septic tank is made from is another major pricing factor that impacts both the upfront cost and long term performance of the system. Common septic tank materials include:
- Concrete:
- Pros: Highly durable, long lifespan, and resistant to most environmental concerns.
- Cons: Heavy, requires specialized equipment for transport and installation.
- Cost: Mid-to-high price range; ideal for permanent installations.
- Polyethylene (Plastic):
- Pros: Lightweight for easier transport and installation, corrosion resistant, and generally more affordable.
- Cons: May require additional installation steps for buoyancy control depending on site conditions.
- Cost: Low-to-mid price range; suitable for most commercial uses.
- Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP):
- Pros: Excellent resistance to corrosion and chemical exposures, making it ideal for environments dealing with hazardous waste.
- Cons: Higher upfront cost compared to concrete and polyethylene.
- Cost: Mid-to-high price range; favored for chemical heavy industries.
- Steel:
- Pros: Extremely strong and able to withstand significant external pressures.
- Cons: Susceptible to rust if not properly treated, and generally the most expensive option.
- Cost: High price range; used in specialty commercial applications where maximum strength is required.
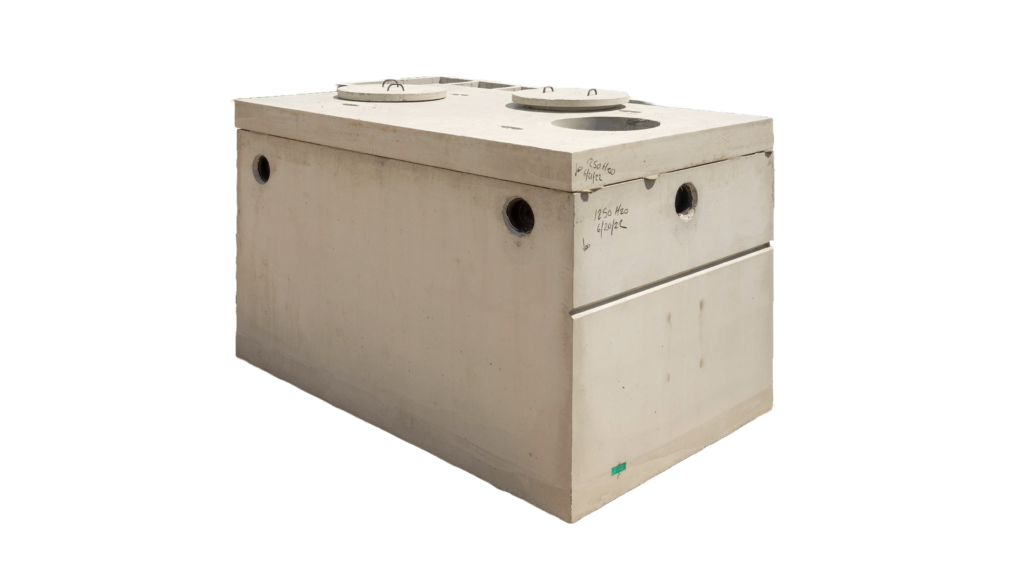
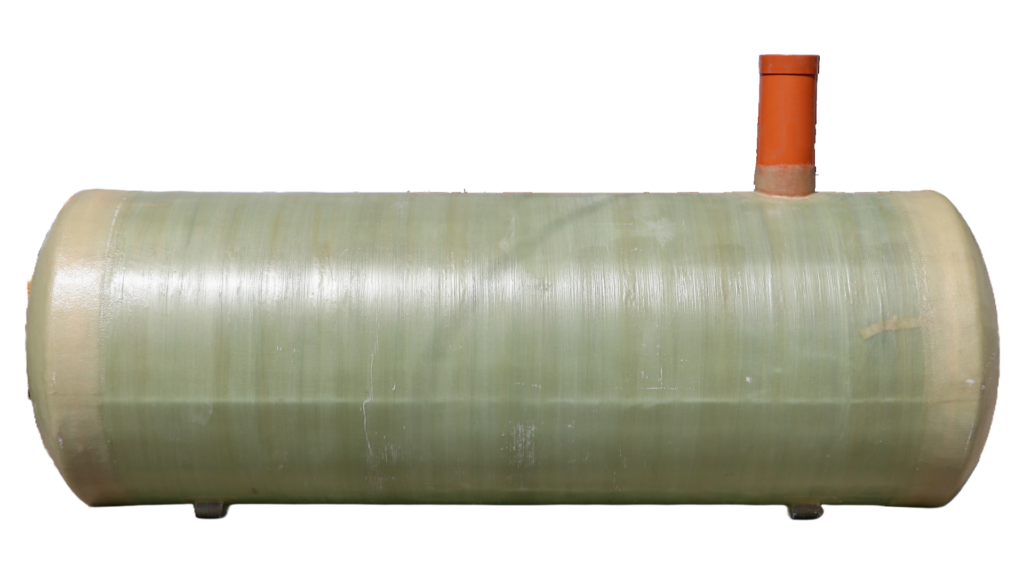


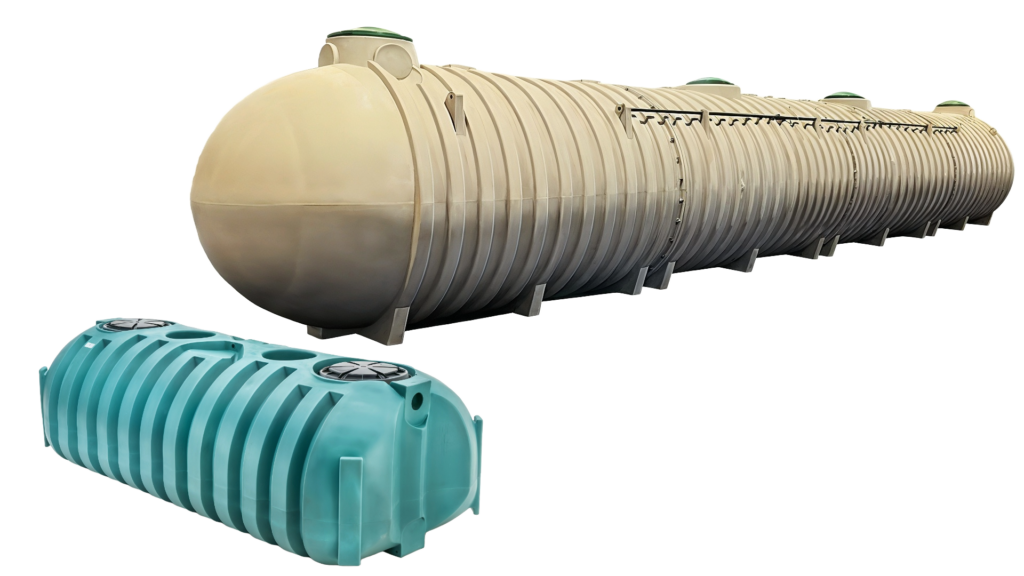
Each material type offers its own cost and performance trade-offs, so it is recommended to choose one that fits both the budget and the operational requirements of the business.
Site Location and Preparation
The site location for where a septic tank is being installed and the amount of additional preparation will have a sizable impact on overall pricing. Here’s a breakdown of location-related cost and considerations:
- Transport Costs:
- Shipping a large septic tank can be expensive, especially for remote or rural locations. Generally, the further the tank has to travel from the supplier, the higher the delivery cost.
- Permitting Fees:
- State and local regulations will require permits, often several types and often also inspections, for installing a septic tank. Fees for these vary widely depending on the area’s environmental restrictions and governmental requirements.
- Site Preparation:
- Preparing the site for installation involves excavation, which can be costly depending on the soil type and terrain. Rocky or clay-heavy soils, for example, require more labor and specialized equipment.
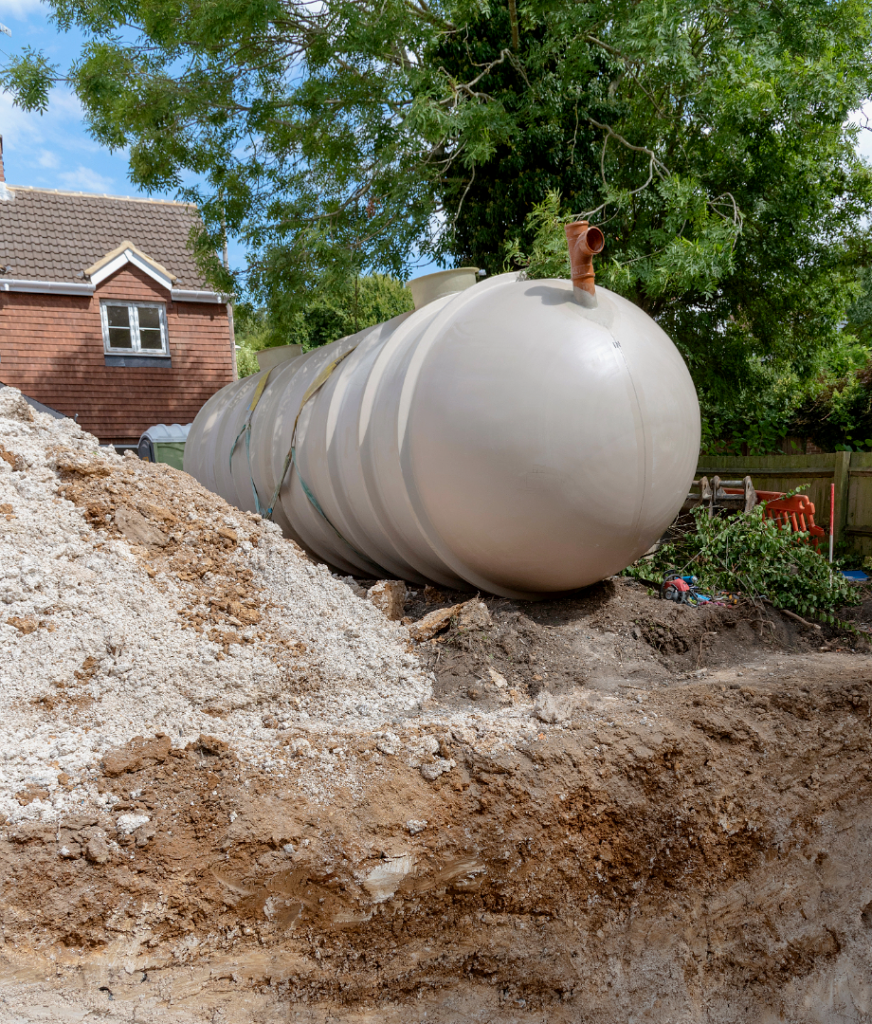

Consider these variables when budgeting to prevent gaps in preparation and unexpected expenses as location can sometimes account for a significant portion of installation expenses.
Tank Features and Customizations
Custom needs and additional features can greatly affect costs, though they often improve the functionality, access, or lifespan of the septic tank. Examples include:

- Double-Wall Construction:
- Adds layers of protection against leaks, ideal for environmentally sensitive areas.
- Chemical Resistance:
- Particularly useful for industries handling hazardous or corrosive substances, such as manufacturing or chemical processing.
- Advanced Plumbing Connectors or Risers:
- Improve accessibility and ease of maintenance but come at an additional cost.
Brand and Supplier
The manufacturer and supplier you choose can also greatly affect price.
- Well Known Brands:
- These often have a higher price due to their reputation for quality, warranties, and proven reliability that has built trust. For polyethylene septic tanks, well known brands include Norwesco, Ace Roto-Mold, and Snyder Industries.
- Lesser Known Suppliers:
- While these may offer lower initial prices, there’s a potential risk of reduced confidence in material quality, manufacturing, or after-sales support.
Selecting a supplier with a trusted reputation is highly recommended as they have often been manufacturing septic tanks for many years, know what works, and offer warranties that cover manufacturing defects. At the National Tank Outlet, we offer commercial grade septic tanks up to 20,000 gallons made in the USA only by the nation’s best manufacturers. A trustworthy brand will ensure your onsite wastewater system will last for years to come.
Types of Commercial Septic Tanks
Commercial septic tanks are available in several materials, each designed to meet different needs based on durability, pricing, and specific applications. Choosing the right material is a key part of ensuring long term performance and value. Below, we’ll explore the most common types of commercial septic tanks and their unique features.
Concrete Septic Tanks
Concrete septic tanks are a popular choice for larger capacity systems, making them a go-to for many commercial properties. Known for their robust construction, these tanks excel in handling substantial wastewater volumes while providing reliable durability.

- Durability:
- Concrete is highly resistant to external pressures and environmental factors, giving it a long lifespan.
- Ideal for permanent installations, particularly in areas with heavy soil or high water tables.
- Pricing Range:
- While concrete tanks are moderately priced, their long term value rises due to their minimal maintenance needs. Prices generally increase based on tank size, with larger systems requiring more material and labor.
These tanks are widely used in industries like hospitality and healthcare, where consistent, large-scale waste management is essential.
Polyethylene Septic Tanks
Polyethylene, or plastic septic tanks, offer lightweight and corrosion resistant alternatives suited for most commercial applications where a conventional concrete tank can be used. Their flexibility and ease of handling make them an excellent and versatile choice.
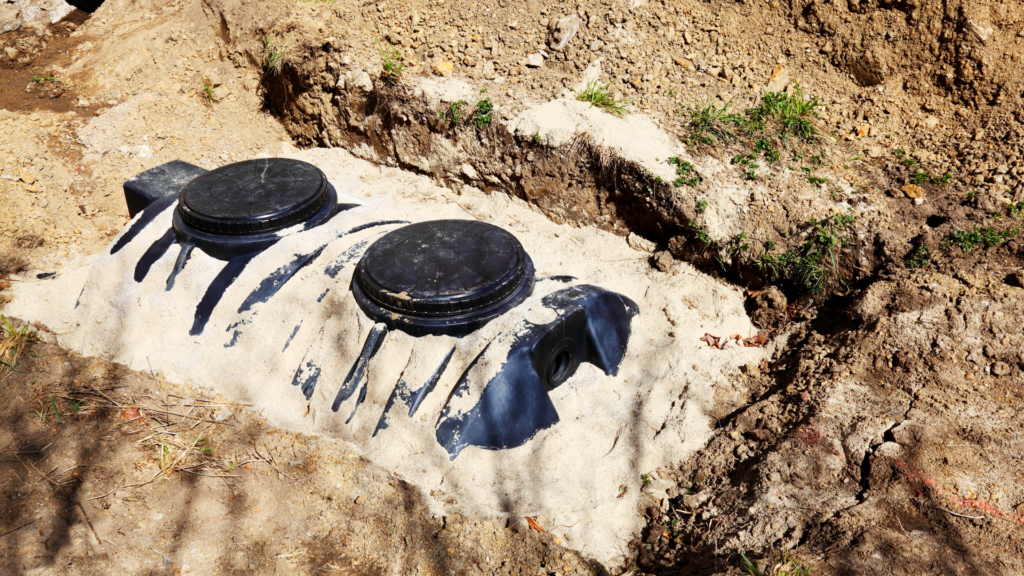

- Lightweight and Corrosion Resistant:
- These tanks are easier to transport and install compared to heavier materials like concrete.
- Polyethylene is immune to rust and corrosion from sewage, ensuring reliable operation even in challenging environments.
- Ideal Use Cases:
- Particularly suited for remote or temporary installations where ease and speed of setup are priorities.
- Pricing Expectations:
- Pricing for polyethylene tanks tends to fall in the lower-to-mid range, making them an economical choice for businesses looking to save money or with tighter budgets.
Polyethylene septic tanks are a practical option for a variety of commercial applications.
Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Septic Tanks
Fiber reinforced plastic, or fiberglass septic tanks, combine the benefits of lightweight construction with resistance to corrosive substances, making them an excellent choice for industries that may have more corrosive or aggressive wastewater.
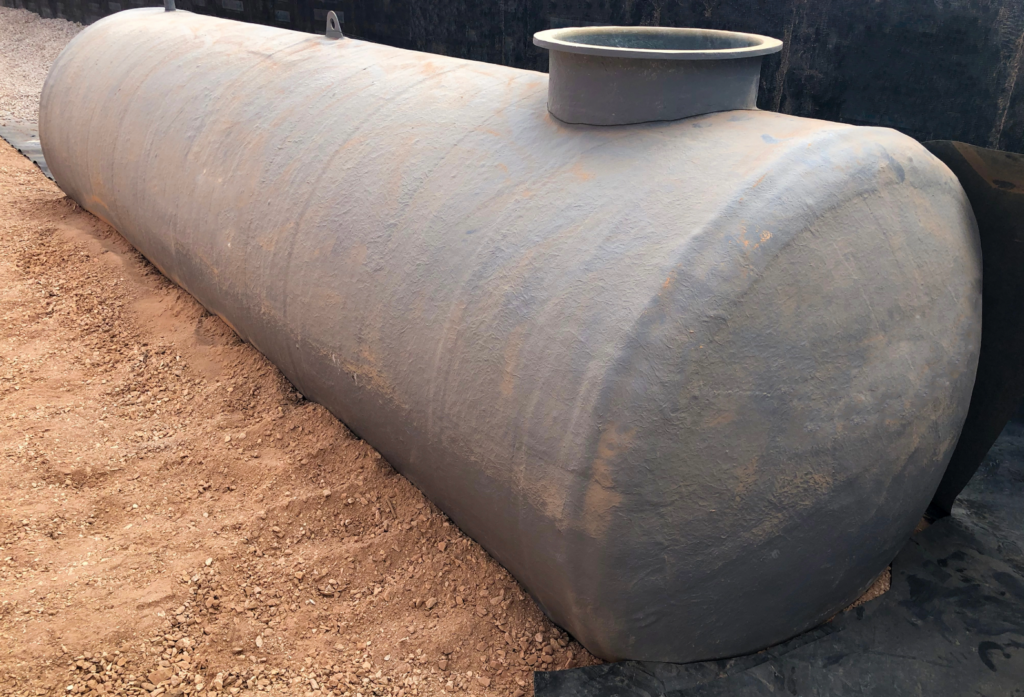

- Advantages in Corrosive Environments:
- FRP tanks are designed to withstand exposure to chemicals and extreme conditions without degrading.
- Their non-porous surfaces reduce the risk of leaks or contamination.
- Cost Comparison:
- While FRP tanks are more expensive than polyethylene and concrete options, they are often more affordable than steel.
- For facilities requiring specialized protection against corrosion, FRP tanks offer a balance between cost and performance.
Frequently used in chemical manufacturing or similar sectors, fiberglass septic tanks can provide the strength businesses need to handle hazardous waste.
Steel Septic Tanks
Steel septic tanks are the heaviest duty option on the market, offering unmatched strength and resilience. These tanks are engineered for commercial applications that require high levels of durability and reliability.
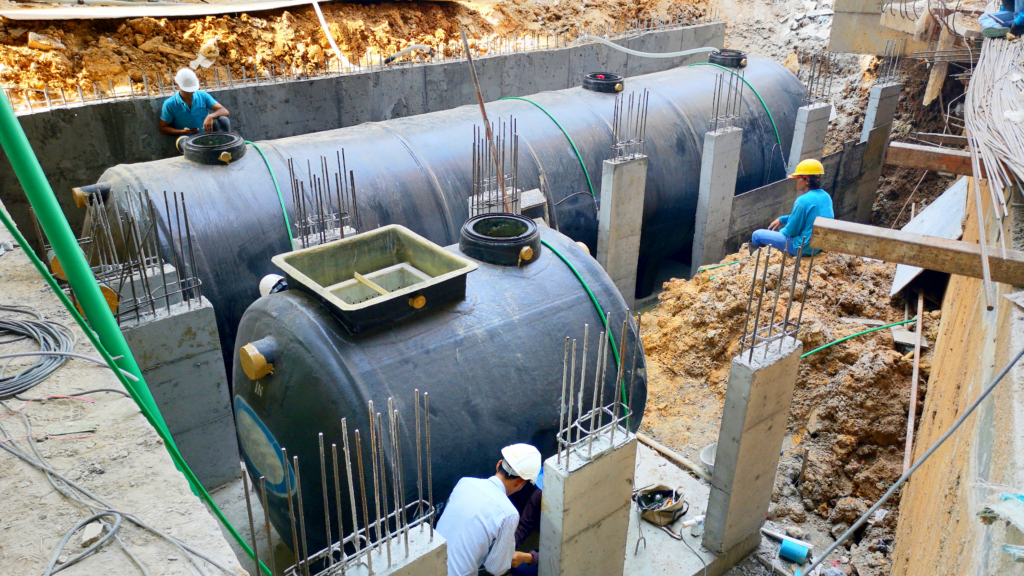

- Strength and Durability:
- Steel tanks can endure considerable external pressures, making them suitable for environments with heavy vehicle traffic or demanding loads.
- With proper coatings and maintenance, they can resist rust and extend their operational lifespan.
- Higher Cost:
- Steel tanks are among the most expensive septic tank options due to their industrial strength construction.
- Due to the cost of production and raw materials, they are often reserved for specific applications.
- Preferred Situations:
- These tanks are ideal for large scale businesses or industrial sites located in extreme climates or environments that require the strongest possible system.
Installation Costs and Considerations
The installation process for a commercial septic tank will involve several steps with each adding to the overall cost. From excavation work, permits, and delivery to plumbing connections, it’s essential to consider everything when planning your budget. Here’s a closer look at the key considerations.
Excavation and Labor
One of the primary expenses in septic tank installation is the labor and equipment required for excavation. Larger commercial tanks, such as those with capacities of 10,000 gallons or more, need heavy duty machinery and skilled operators to prepare the site.
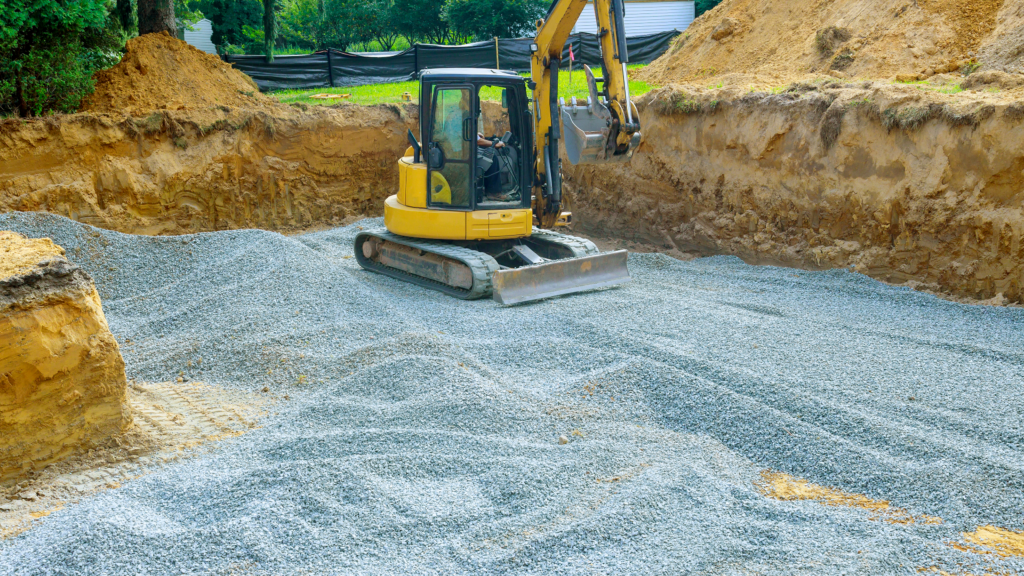

- Labor Costs:
- Excavating the ground for a large tank requires construction crews experienced in handling industrial scale projects. The cost of labor will vary depending on the region and the complexity of the job.
- Heavy Equipment:
- Bulldozers, backhoes, and cranes may be needed, particularly for heavy tanks like those made of concrete or steel. Rental costs for this machinery add to the project’s total.
- Impact of Soil Conditions:
- The type of soil can significantly affect excavation expenses. Rocky terrain, clay soils, or areas with a high water table often make additional preparation necessary, increasing both time and cost.
Proper planning and site assessments are essential to avoid unexpected delays and overshooting budgets during this phase. Experienced contractors or engineering firms can typically provide a reliable site evaluation and cost estimate.
Plumbing and System Integration
Installing the septic tank is just the beginning. After placement, it must be integrated into the property’s wastewater system. Plumbing connections and auxiliary components will have their own additional costs.

- System Integration Costs:
- This process involves linking the septic tank to the property’s wastewater lines. The complexity of this task will depend on the location of the tank relative to the building’s plumbing system.
- Additional Expenses:
- You may need to purchase and install distribution boxes, risers, or pumps, depending on the design and layout of the septic system. These components improve system performance and accessibility for maintenance but come with added costs.
Businesses should work with experienced contractors to ensure proper alignment and installation of all system components.
Inspection and Permitting Fees
Compliance with local and state regulations is mandatory when installing a commercial septic tank. Inspections and permits can add to the overall cost but are necessary to ensure the system is located, designed, and will operate within legal standards.

- Regional Variations:
- Permitting costs vary widely depending on the state or municipality. Areas with stricter environmental laws may charge higher fees or enforce additional requirements.
- Importance of Compliance:
- Scheduling inspections will ensure the installation meets all safety and environmental regulations. Failing to comply with these standards can lead to fines or system modifications, driving up costs further.
Factoring permitting and inspection fees into your budget early in the planning process can prevent surprises down the road.
Timeline for Installation
The time it takes to install a commercial septic tank can have a direct impact on expenses, particularly as it is a labor intensive project.
- Labor and Equipment Costs:
- Longer installation timelines will mean higher labor costs, as construction crews and equipment must remain on-site for extended periods.
- Project Delays:
- Unanticipated challenges, such as poor weather or difficult terrain, can extend the timeline and increase expenses. Efficient project management is key to minimizing delays.
Planning ahead and working with reputable contractors can help ensure the installation process stays on schedule and within budget. Proper preparation not only helps control expenses but also ensures a smooth and compliant installation process.
Maintenance and Associated Costs
Maintaining a commercial septic tank is a key part of ensuring its longevity and continued operation. Proper upkeep will minimize unexpected expenses and help businesses comply with any environmental regulations. Here’s what you need to keep in mind about maintenance and associated costs.
Pumping and Cleaning
Regular pumping and cleaning are essential to keep large capacity septic tanks functioning. Over time, solid waste will accumulate in the tank and reduce its storage capacity. If not removed, this can potentially lead to blockages or system failures.

- Frequency of Maintenance:
- For large capacity septic tanks used in high volume commercial applications, professional pumping is typically required every 1 to 3 years. The exact timing will depend on how much the system is used and the volume of wastewater produced.
- Average Costs:
- Pumping and cleaning services for large septic tanks generally cost between $300 and $600 per visit. However, commercial tanks with capacities over 10,000 gallons will have higher fees due to the additional equipment and labor required.
Having regular cleaning scheduled not only extends the life of your septic system but also prevents costly repairs caused by neglect or overfilling.
Repairs and Replacements
Even with regular maintenance, occasional repairs or replacements may be needed to address wear and tear or unexpected problems. Understanding potential costs can help businesses plan for these long term expenses.
- Common Repair Costs:
- Repairs for leaks, cracks, or malfunctioning components can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on the extent of the damage and the material of the tank. For example:
- Fixing small leaks in concrete tanks may cost around $500 to $1,000.
- Replacing damaged pumps, pipes, or fittings can add $500 to $2,000 to repair expenses.
- Repairs for leaks, cracks, or malfunctioning components can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on the extent of the damage and the material of the tank. For example:
- Lifespan of Materials:
- Different tank materials have varying lifespans that affect replacement timelines and costs:
- Concrete Tanks: Long lasting, with lifespans of 40 years or more when properly installed and maintained.
- Polyethylene Tanks: Generally last 20 to 30 years or more when properly installed, maintained, and protected from external forces.
- Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Tanks: Resistant to corrosion, offering durability of 30 to 50 years.
- Steel Tanks: Can last 20 to 30 years but require liners and may need maintenance to avoid rust-driven deterioration.
- Different tank materials have varying lifespans that affect replacement timelines and costs:
Environmental Compliance and Inspections
To protect the environment and avoid legal issues, it is often non-negotiable to maintain compliance with local and state regulations. This may involve regular inspections and confirmation of proper use.
- Ongoing Compliance Costs:
- Environmental compliance may involve periodic testing, approval fees, and documentation, which can cost $300 to $500 annually for commercial properties. These costs and requirements can vary depending on your state’s specific regulations.
- Benefits of Regular Inspections:
- Routine inspections help identify potential problems early thereby preventing larger and more expensive issues down the road.
- Compliance ensures that businesses avoid hefty fines or penalties for violating environmental laws, which can easily exceed $1,000 per infraction.
Investing in professional inspections will not only minimize the risk of shutdown to daily operations but also reinforce your commitment to regulations and our shared environment.
By understanding the costs and long term considerations associated with maintenance, businesses can take this to create a proactive plan to keep their septic systems running smoothly for years to come while avoiding expenses that could be avoided.
Tips for Budgeting and Reducing Costs
Investing in a commercial septic tank is a significant financial decision. Careful planning and strategic choices can help businesses stay within budget. Here are some practical tips to consider.

Plan Ahead
A well-thought-out plan will help avoid costly surprises during the purchase and installation process.
- Avoid Unexpected Expenses:
- Start by identifying all potential costs, from excavation and installation to maintenance and inspections. Overlooking any of these can lead to budget overruns.
- Have site-specific factors such as soil type, terrain, and regulatory requirements fully assessed with recommendations to prevent delays and added costs.
- Work with Experienced Professionals:
- Hiring contractors with expertise in commercial septic systems can help ensure accurate cost estimates and project management.
- Professionals can also guide you in selecting the most suitable tank type and features for your property.
Planning ahead not only keeps your project on track but also allows you to allocate resources more effectively.
Compare Quotes and Suppliers
Taking time to compare multiple quotes and suppliers can help you save money without compromising on quality.
- Request Multiple Quotes:
- Reach out to several suppliers and contractors to get detailed pricing for tanks, materials, and installation services. This comparison can give you a clearer understanding of market rates and allow companies to compete with each other for your business.
- Negotiation Tactics:
- Bundling or combining services, such as designing with installation and even maintenance, may help you secure better rates.
- Highlighting your business’s long-term needs can encourage suppliers to offer discounts or additional perks.
Remember, the lowest price isn’t always the best choice. Ensure the supplier or contractor has a solid track record of reliability and quality.
Financing Options
For many businesses, financing can ease the burden of upfront costs and make large purchases more manageable.
- Supplier Financing Plans:
- Many suppliers offer flexible payment plans that allow businesses to spread costs over months or years. Look for plans with low or zero interest rates to maximize affordability.
- Government Grants or Incentives:
- Depending on your industry and location, you may qualify for grants or tax incentives that reduce the cost of a septic system installation. The best way to determine if you qualify for anything is to contact your local or regional government department that oversees onsite sewage systems.
Exploring financing options can help you secure a system that meets your needs without straining your immediate resources. Smart budgeting lays the groundwork for a septic system that will serve your property’s needs reliably for years.
FAQ Section
To make budgeting and planning for your commercial septic tank easier, here are answers to some commonly asked questions.
1. How do I determine the right size septic tank for my property?
The size of your septic tank will depend on several factors, including the volume of wastewater your property generates, the number of people or units using the system, and industry-specific requirements. Engineers or contractors can perform a flow rate analysis to determine the gallons per day (GPD) your system needs to handle. For high usage commercial properties, tanks can range from 5,000 gallons to upwards of 20,000 gallons which may require multiple tanks.
2. What are the signs that my septic tank needs maintenance?
Some common signs include:
- Slow drains or backups in sinks, toilets, or floor drains.
- Unpleasant odors near the tank or drain field.
- Pooling water or consistently soggy soil in the area around the tank.
- An observed increase in wastewater levels within the tank during inspections.
Scheduling regular pumping and inspections can help avoid costly damage.
3. How long does it take to install a commercial septic tank?
How long a septic tank takes to install will vary depending on the size of the tank, soil conditions, and permitting requirements. On average, installation can take 1 to 2 weeks. However, challenging terrain, poor weather, or unexpected site preparation needs can extend this timeline. Working with experienced contractors and planning ahead can help keep the project on schedule.
4. Are there government incentives for installing commercial septic systems?
Yes, depending on your location and industry, there may be grants, tax credits, or low-interest financing programs available for commercial septic system installations. These are often tied to environmental initiatives or rural development programs. To learn more, check with your local or regional government agencies or reach out to organizations that support sustainable wastewater management.
5. What is the average lifespan of a commercial septic tank?
The lifespan of a septic tank depends on the material and maintenance. For example:
- Concrete Tanks: 40+ years if properly maintained.
- Polyethylene Tanks: 20 to 30 years or more when installed correctly.
- FRP Tanks: 30 to 50 years due to their corrosion resistance.
- Steel Tanks: 20 to 30 years, provided they are coated and maintained to prevent rust.
Regular inspections, cleaning, and repair of components can extend the life of your tank.
6. How much does it cost to maintain a large capacity commercial septic tank?
The cost of maintenance varies depending on tank size, use, and location. On average:
- Pumping and Cleaning: $300 to $600 per visit, with larger tanks costing more.
- Annual Inspections: $300 to $500.
- Repairs or replacements for components like pumps or pipes can range from $500 to $2,000.
Investing in routine maintenance helps avoid expensive repairs or replacements later.
7. Can I install a commercial septic system in an urban area?
Yes, but additional considerations may apply due to space constraints, higher permitting fees, and local regulations. Consulting with professionals familiar with urban requirements is highly recommended for a successful installation.
If you have more specific questions or need guidance on selecting the right septic tank for your business, the experts at National Tank Outlet are ready to help. Reach out today to discuss your project.
Takeaway
Navigating the costs of commercial septic tanks requires a thorough understanding of the different parts at play:
- Factors Influencing Pricing: From tank size and material to location and custom features, multiple points contribute to the total cost of a commercial septic system.
- Types of Tanks: Understanding the differences between standard concrete, polyethylene, fiber reinforced plastic (FRP), and steel tanks and their general price ranges will help you select the best option for your needs and budget.
- Installation and Maintenance Costs: Proper planning for excavation, plumbing connections, and regular pumping will keep your system functional and compliant.
- Budgeting Tips: Strategic planning, comparing suppliers, and exploring financing options can help reduce costs.
By considering these points made in this guide, business owners can make more informed decisions for their property and budget. If you’re looking for guidance in choosing a septic tank for your commercial property or are looking to compare quotes, the team at National Tank Outlet is here to help; contact us today to discuss your needs.
Note: Any pricing information within this article is for informational purposes only. They are approximate and/or estimated values based on current, available market data. Prices presented herein are not provided as a guarantee of personal results as costs vary by location, supplier, contractor, and various economic factors, but are offered in good faith as a helpful estimation of potential expenses in expectations, planning, and budgeting.