
Protecting municipal water infrastructure—and the communities it serves—sometimes requires more than traditional tank solutions. From treatment facilities to distribution networks, every component must be robust and reliable. Municipalities face greater regulatory scrutiny and require environmental safeguards to prevent leaks and releases, often through the use of secondary containment measures. Chemical storage, in particular, introduces significant risks. Leaks, contamination, and environmental hazards can result in costly cleanups, regulatory fines, and loss of public trust. Double wall tanks are an excellent way to achieve secondary containment and protection against these potential safety concerns.
Let’s look at how double wall tanks can provide security with better safety, simplify compliance, and improve operations for municipal water systems. Backed by current regulations and data, our guide aims to help municipal professionals and contractors in considering their options.
1. What Are Double Wall Tanks?
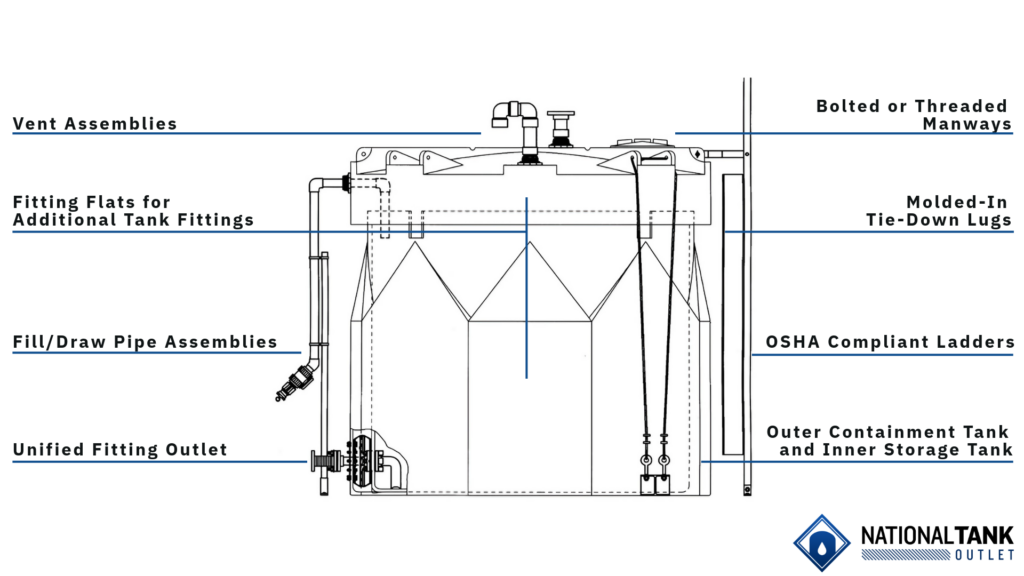
Double wall tanks, also known as dual containment tanks, use a “tank-within-a-tank” design. This engineering offers greater protection than traditional single wall tanks and makes them ideal for storing hazardous or sensitive liquids.

Definition
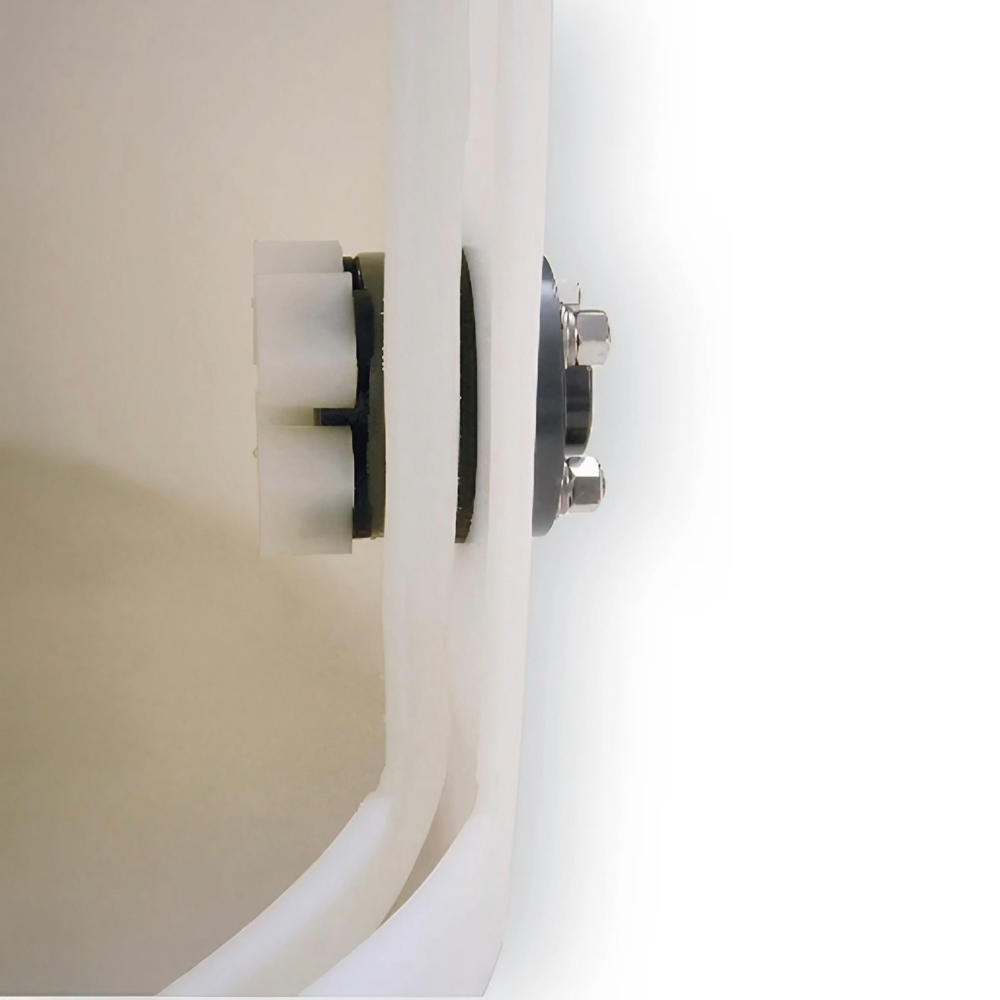
A double wall tank has a primary inner tank for holding liquids and a secondary outer tank that acts as a containment basin. If the inner tank is breached, the outer tank is designed to expand the container’s total capacity to at least 110% of the contents, complying with EPA Secondary Containment Requirements (40 CFR Part 264.193).

Key Features
- Secondary Containment: Outer tank capacity is typically 10 to 20% of the inner tank to provide a total 110 to 120% storage containment with the primary tank to meet or exceed EPA and many state regulatory requirements.
- Seamless Construction: Most are made using a rotational molding manufacturing process for the inner and outer tanks to create a durable, one piece structure without seams or joints that reduces potential failure points.
- Advanced Materials: Commonly made from High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) or Cross Linked Polyethylene (XLPE), where both offer strong chemical resistance and include UV inhibitors for durability against sunlight degradation that makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
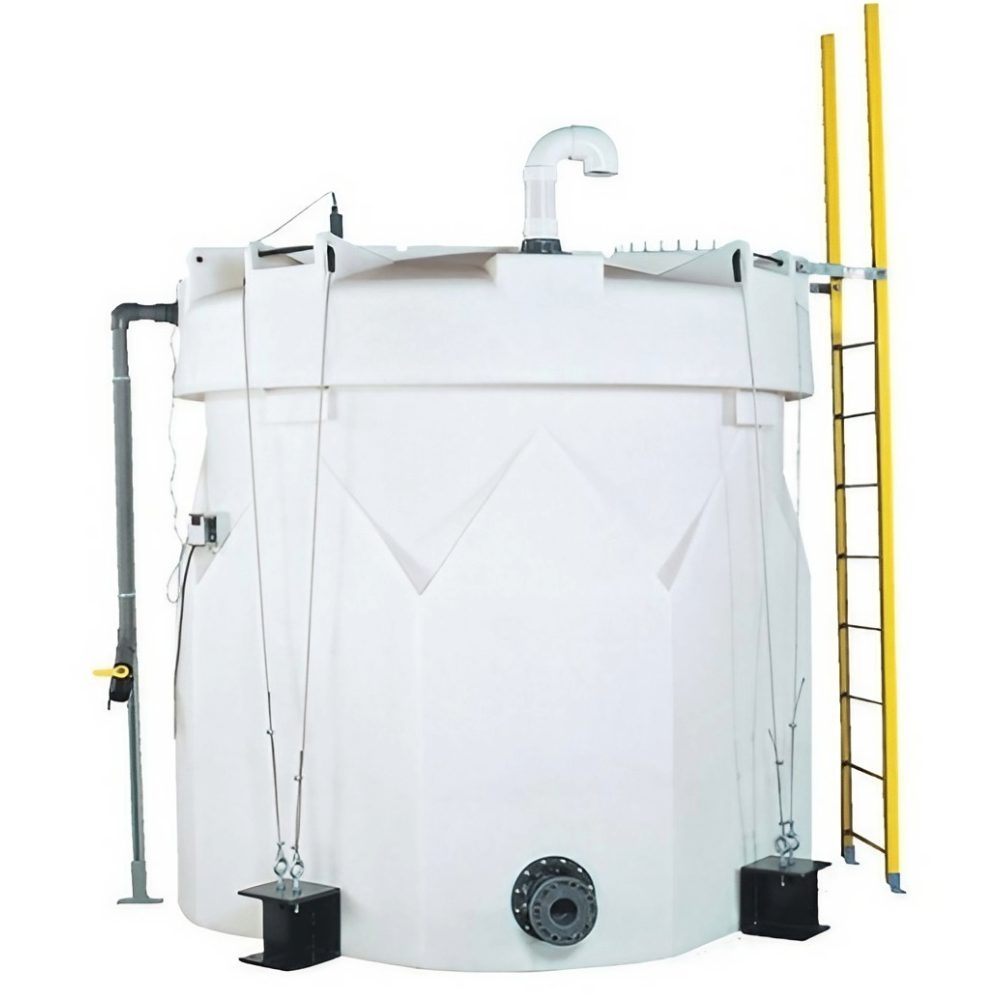
Applications
Municipalities often use double wall tanks to store water treatment chemicals (such as sodium hypochlorite) and to manage wastewater before processing. Municipal case reports report low to zero environmental incidents after replacing aging single wall tanks with double wall systems.
2. How They Can Improve Municipal Water Safety
Double wall tanks are standard storage tanks with a proactive safety measure built-in. By design, they address the most common points of failure in liquid storage, with the result—greater peace of mind for municipalities.
Leak Prevention
The primary benefit of a double wall tank is its built-in spill containment. The outer wall acts as a comprehensive barrier: if the primary tank leaks, the contents remain safely contained until it can be managed. This prevents hazardous chemicals from reaching the ground where it can contaminate soil and groundwater or create a safety risk for people. Many municipalities choose to include integrated leak detection systems for entry-less monitoring and rapid response times. According to an EPA summary of reported chemical storage failures, double wall tanks reduce spill incidents by over 90% compared to single wall tanks with external dikes.
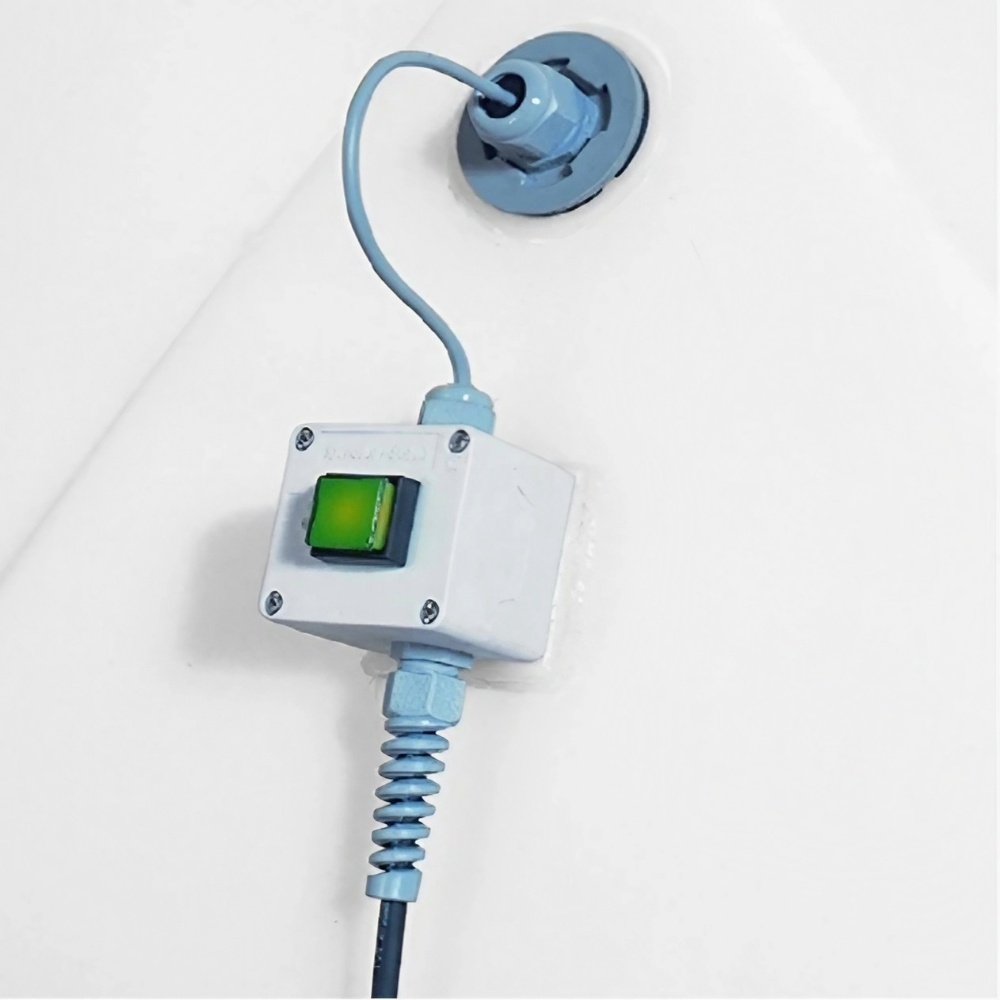
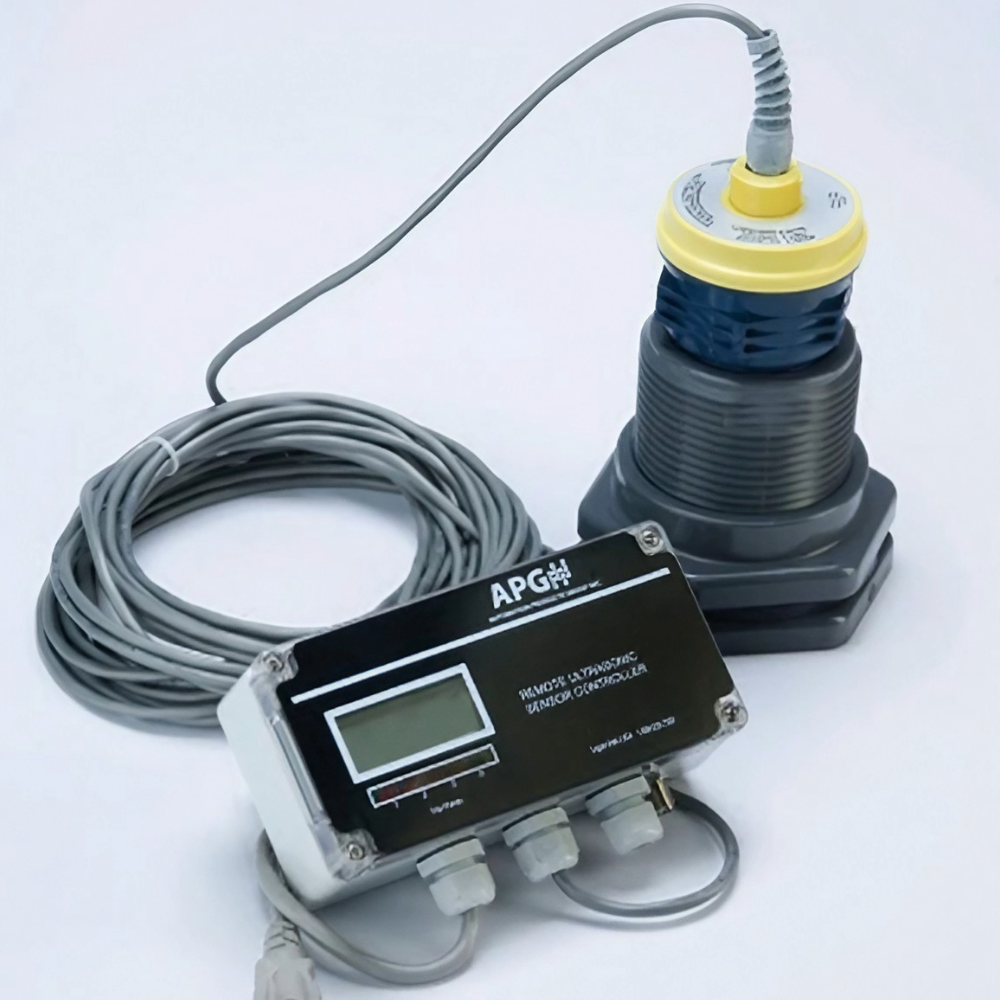


Contamination Control
Seamless, rotationally molded tanks limit joints and failure points where leaks could result in environmental releases. For potable water applications that include chemical injection, NSF/ANSI 61 certification ensures the tank materials do not leach harmful substances, which is a regulatory requirement in most U.S. states. Independent tests of these products have confirmed undetectable levels of chemical leachate from certified HDPE tanks.
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental regulations (e.g., EPA SPCC Rule, 40 CFR Section 264) mandate secondary containment for certain hazardous materials. Double wall tanks are engineered to ASTM D-1998 standards and built for compliance to simplify permitting and inspections. Municipal compliance audits may flag externally contained single wall tanks as high risk and recommend they be replaced with self contained double wall systems. Using these tanks can help municipalities avoid potential fines that can exceed $45k to $700k+ per incident.
Want to learn more about how double wall tanks can prevent leaks and ensure compliance? Contact us for more details.
3. Environmental, Operational Benefits
Safety commitments bring operational and environmental rewards. Double wall tanks are a smart investment that can contribute to protection efforts for communities and improve the overall workflow and sustainability of municipal systems.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Double wall tanks’ primary function is to prevent spills. EPA data shows 75% fewer environmental cleanup incidents in facilities that use heavy duty double wall systems versus those with only single wall tanks and external concrete dikes. Many lifecycle analyses find HDPE and XLPE tanks to last longer and are more recyclable than steel or concrete alternatives. Fewer replacements mean less landfill waste and lower impact over time to the environment.
Work Efficiency
Double wall tanks offer a compact, all-in-one solution that simplifies the facility design process. Since secondary containment is built into the tank, installation space, cost, and project duration are reduced. Advanced options, such as digital monitoring for leaks and inventory management, can further cut labor costs and reduce manual error, in addition to improving response times. Facilities with high turnover or small staff can greatly benefit from such automation.
4. Versatile and Scalable for Municipal Applications
Double wall tanks are versatile. They can be used for several municipal applications and are scalable to match different system sizes. Their ability to safely store commonly used chemicals means they can be deployed across various stages of the water management cycle—the result: a single, reliable solution for multiple needs.
Potable Water Storage
HDPE double wall tanks are certified to NSF/ANSI 61 and pass FDA standards to meet U.S. potable water regulatory requirements. Small towns typically use 1,000 to 5,000 gallon tanks, while large urban systems may require up to 100,000 gallons or more. For built-in secondary containment, commonly available double wall tanks’ sizes range up to 20,000 gallons. While plausible, double walled tanks are the least efficient option for potable water storage, due to cost and availability of other products.
Chemical Storage
Water treatment facilities rely on a range of chemicals, many of which are corrosive or harmful to people at concentrated levels. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite, ferric chloride, and hydrofluosilicic acid. Double wall tanks made of high density and cross linked polyethylene are rated for these substances (see manufacturer chemical compatibility charts). This chemical compatibility improves the structural integrity of the tank over its lifespan and works to prevent dangerous leaks and ensure the safe containment of chemicals essential for water purification. Chemical storage applications are the primary use where double wall tanks really excel.
Wastewater Management
Before wastewater can be treated and safely discharged, it must be securely contained. Double wall tanks can be used for temporary wastewater storage. Built in manways and fittings allow for easy inspection and cleaning. With options for different manway sizes and fittings, these tanks can be customized to improve access for inspection, sampling, and cleaning, which will ultimately streamline the maintenance activities of municipal workers.
Scalability
Whether serving a rural township or a major metropolitan area, double wall tanks can be set up and connected in unison via piping systems to increase total storage volume.
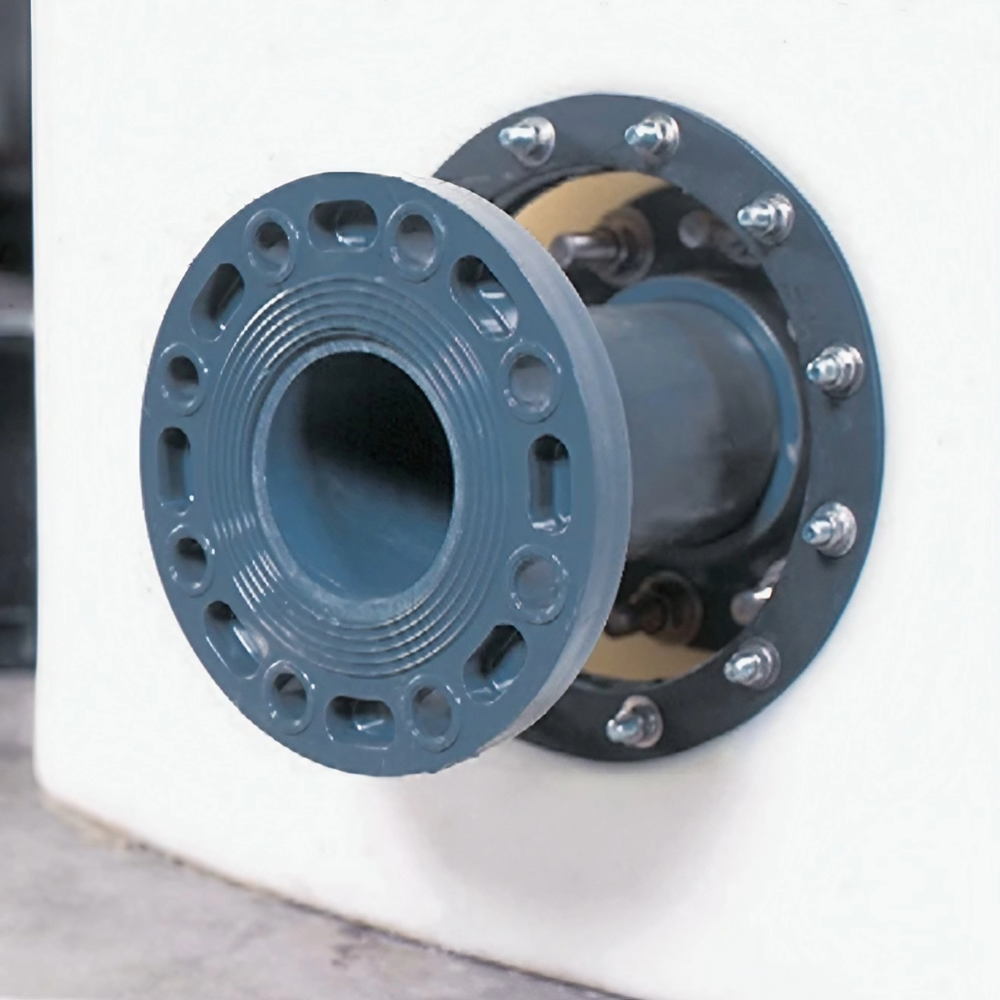

5. Addressing Common Concerns
Now that we’ve addressed the benefits of double wall tanks, we should point out their potential drawbacks and certain considerations about cost, customization, and durability.
Cost vs. Value
Initial purchase price for a double wall tank is typically 20–40% higher than a similar capacity single wall tank. However, eliminating the need for external concrete dikes or other secondary containment options can lower installation costs. For example, a 10,000 gallon system may save $7,000–$11,000 when factoring in the labor and construction costs for external secondary containment. Long term, municipalities that use double wall tanks report savings from spill prevention, lower insurance rates, and fewer regulatory fines—costs that can easily offset the higher upfront investment within a few years.
Customization Options
Manufacturers typically offer a range of customization options: various manway sizes, fittings, chemical compatibility linings, and electronic monitoring. This flexibility allows the tanks to be custom-matched to specific applications and municipal needs. However, these, often necessary, customizations come at an additional cost that buyers should be aware of and prepared for.
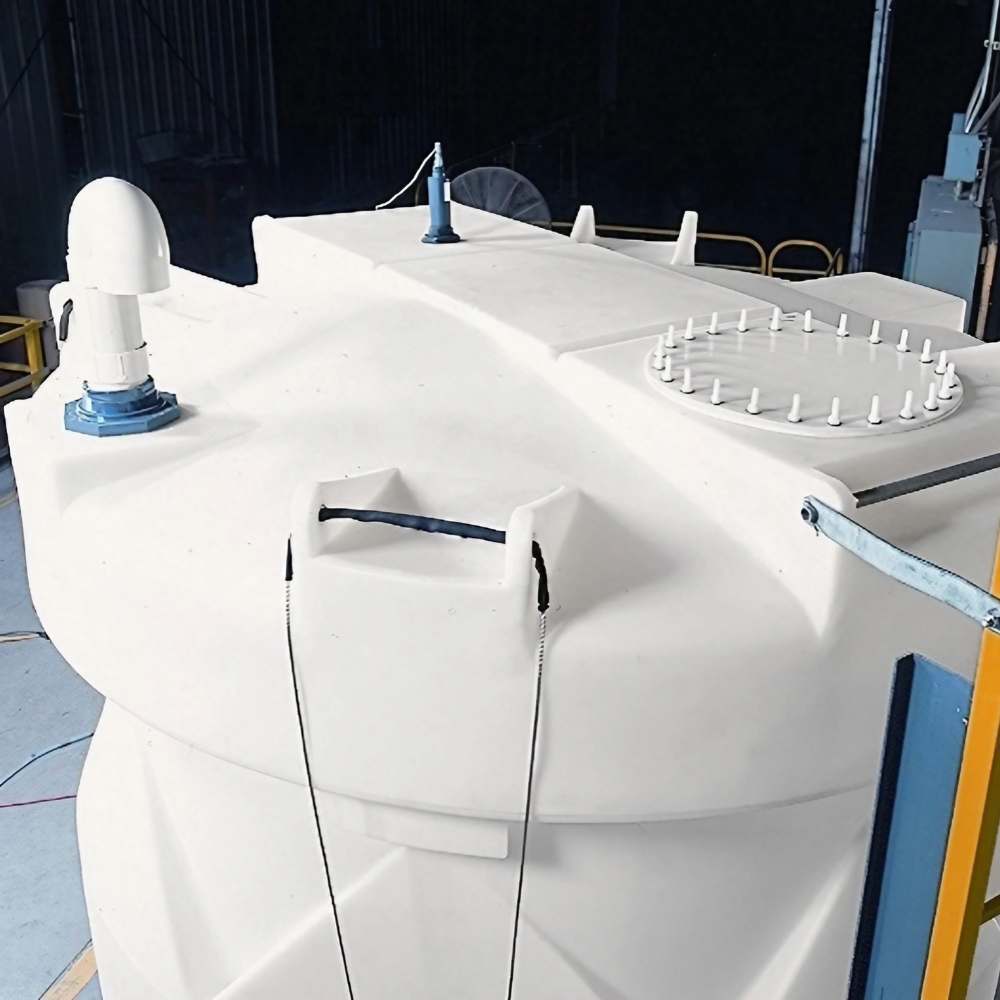


Durability Against Harsh Conditions
Most municipal infrastructure must be able to withstand the elements year-round. Double wall tanks are engineered with this in mind. Built from high quality polyethylene that includes UV stabilizing compounds, they resist the degradation that can occur from direct sunlight and are approved for outdoor installations. These materials are also designed to perform reliably across the range of common ambient temperatures, from freezing cold to intense heat to deliver consistent and safe operation across different climates. For further conditioning and environmental durability, double wall tanks can be insulated and equipped with heat tracing equipment.
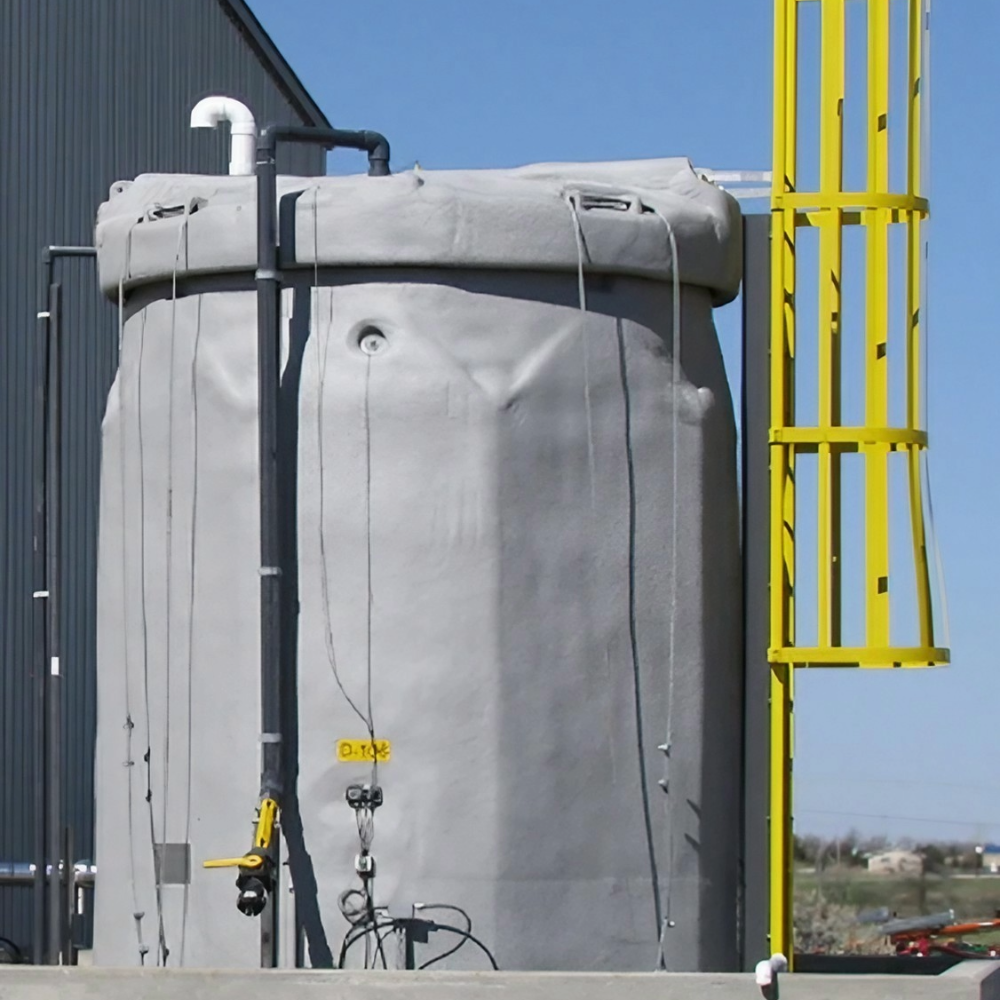
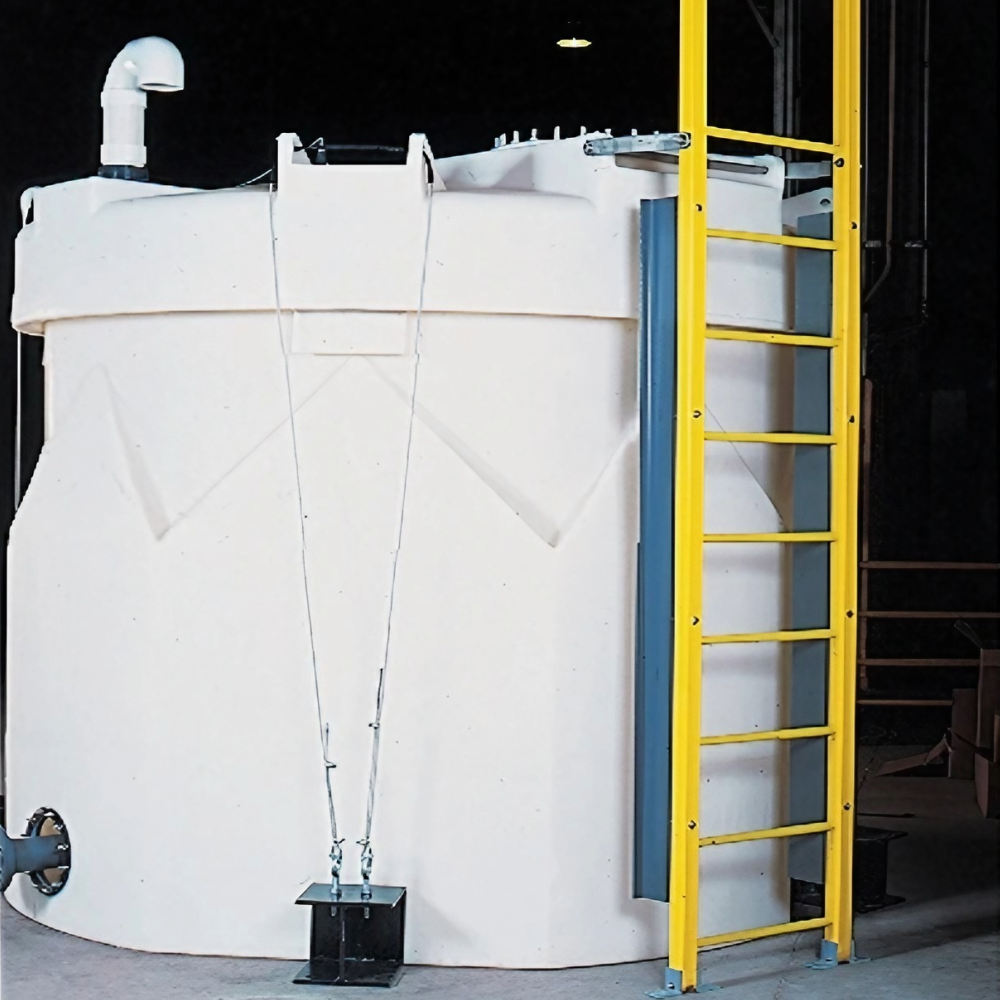


Potential Drawbacks
- Maintenance: Double wall tanks require regular inspection of the interstitial space (the gap between walls), especially if a leak detection system is not used. Sediment buildup or sensor malfunction can occur if not periodically checked.
- Chemical Compatibility: Some harsh or unique chemicals may not be compatible with HDPE or XLPE; always confirm with a chemical compatibility chart.
- Long Term Climate Exposure: While UV inhibitors extend life for outdoor installations, extreme climates (very high or low temperatures) may still affect tank longevity. Secondary containment integrity should be checked annually.
Double the Walls, Double the Guard, Protect Your Community
Reliable, compliant, and long term money saving storage is essential for safeguarding municipal water systems. Double wall tanks deliver appreciable benefits in spill reduction, compliance, environmental protection, and overall operations. They scale from small towns to large cities and are a proven investment in water system safety.
Take the Next Step
Ready to upgrade your municipal water storage?
Contact our experts today for a free consultation and custom quote or browse our selection of double wall tanks. Don’t wait, upgrade your municipality’s safety with the most reliable double wall tanks available—the Captor™ tank-in-a-tank made right here in the USA from Snyder Industries, one of North America’s most trusted and respected tank manufacturers.